Techinfo
Technical Information
Ferrite Cores
What is a Ferrite Core?

Ferrite cores are mainly metal oxides that exhibit ferromagnetism and are electrically insulating, so they are widely used as magnetic materials for high frequencies.
Soft ferrite is a mixed ferrite whose main component is iron. By using this ferrite as the magnetic core of the toroidal core (donut-shaped core), it can block high-frequency currents that cause noise radiation.
When a ferrite core is attached to the cable through which noise current is flowing, the core becomes magnetized and increases the impedance of the cable and accordingly reduces the propagation of noise current. By magnetizing the core, it absorbs noise energy and converts it into heat.
In order to suppress radiated emissions at frequencies above 30 MHz, bead-shaped cores using Ni-Zn-based soft ferrite are often used. Many of them are applied on cables of electrical and electronic equipment such as personal computers and digital home appliances.
Characteristics of Ferrite Cores

Noise suppression effect of the ferrite core is determined by the impedance.
The impedance characteristics of ferrite cores are expressed by the following formula:
Z = z×shape factor×N2
Z = impedance, z = material properties, shape factor = cross-sectional area÷ average path length
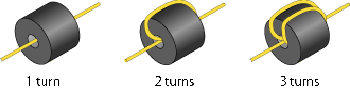
N = number of turns
※Ferrite uses materials with optimal properties at frequencies 30 MHz or more.
※By turning the wire, the frequency band shifts to a lower frequency.
How to Select Appropriate Ferrite Cores
There is a wide range of variations of ferrite cores for EMC management, and they can be used in a variety of situations.
1. When to use split cores
a. When applying cables that already have connectors attached.
b. When installing a ferrite core makes it difficult to automate the connector assembly Depending on the total cost, split cores are used.
c. When cores are required to be fixed.
2. Selection by sizes and shapes
a. As a guideline, in the case of noise reduction in the frequency band higher than 150 MHz, and when the cable is not turned.
・Choose a core with the inner diameter large enough for the cable, the outer shape large as possible, and the length (L) long.
・The cable is not turned when used.
・Impedance characteristics can be obtained by the shape factor.
b. As a guideline, in the case of noise reduction below 150 MHz or when used for cables in a device.
・Choose a core with the inner diameter large (a size that allows for several turns of the cable) and the length (L) short.
・The cable is turned when used.
・Impedance characteristics can be obtained by the number of turns.
※Since the appearance deteriorates by turning a cable, it is often used for cables in devices.
3. Selection by types of cables
・Flat cables: SSC series
・FFC cables: FPC series
・Multi-core cables: TR series, RI series, etc.
Applications of Ferrite Cores

・Used for suppressing radiated noise from cables
・Measures against static electricity
Static electricity contains noise components with a wide range of frequencies depending on the speed at which the voltage is applied.
In some cases, it can be useful for noise at 30 MHz or higher can be cut.
・Measures against internal EMI

